After the success of Chandrayaan 3 India’s ISRO and Japan’s JAXA are getting ready for LUPEX (Lunar Polar Exploration) to find the answer to the question Is there water on the moon? This mission is scheduled for 2028 as Chandrayaan 5 mission.
India became the fourth country to achieve a soft and precise landing on the Moon with ISRO’s Chandrayaan-3 lander successfully touching the lunar surface. Japan followed as the fifth nation to accomplish a successful lunar landing with JAXA’s SLIM mission.
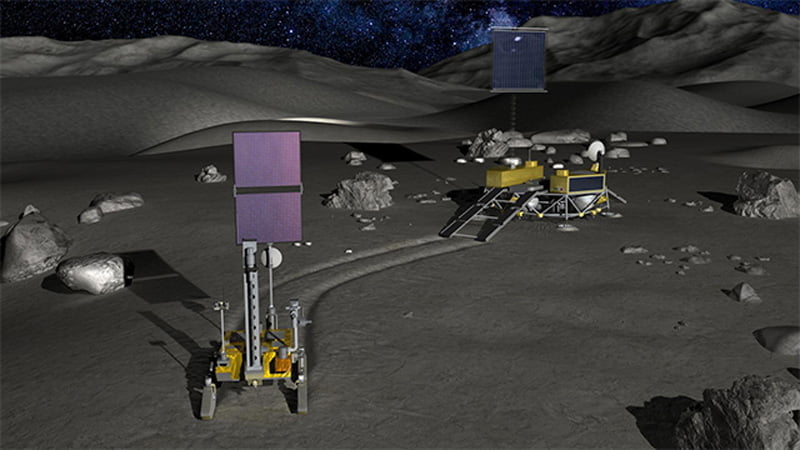
India and Japan collaborating on a new lunar mission called LUPEX or Chandrayaan 5. This mission will be near the South Pole where no sunlight reaches and the temperature is also very low to survive any rover.
Read also Aditya L1: India’s 1st Mission to Sun
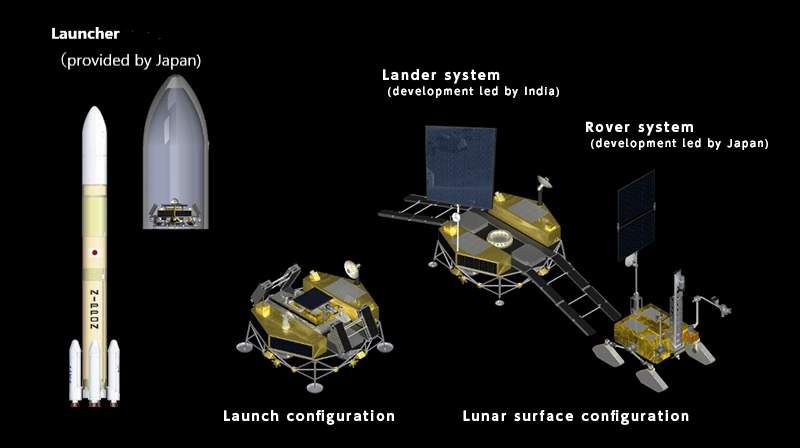
This mission would be an uncrewed Lunar Lander and Rover mission, JAXA will provide the launch vehicle H3 and rover while ISRO will provide the Lander.
The Objective of LUPEX
The primary objective of the Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX) is to explore the polar regions of the Moon to understand the presence of water and its potential usefulness. The mission aims to fulfill this objective through two main approaches: assessing the quantity and quality of lunar water resources.
The quantity approach accurately determines the actual amount of water present in the predicted areas based on existing observational data. By gathering on-site measurements and obtaining “ground truth data,” LUPEX will provide a crucial reference line for calculating how much water needs to be transported from Earth for future lunar missions and how much can be sourced locally. This data could bring about revolutionary changes in lunar exploration economics and sustainability.
The quality approach aims to understand the distribution, conditions, and forms of lunar water resources through on-site observations in the polar regions of the Moon. It’s important to comprehend these criteria to effectively utilize lunar water in various capacities such as life support and propulsion.
Important facts
| Launch Year | 2028 |
| Launch vehicle | H3 rocket (provided by Japan) |
| Orbit | KAGUYA Launch orbit |
| Launch Mass | 6 tons |
| Rover mass | 250 kg |
| Life Span of Mission | more than 3 months |
| Landing Point | Near the South Pole of the moon |
Instruments for LUPEX
| (1) Resource Investigation Water Analyzer (REIWA) REIWA consists of three instruments [JAXA] | (a) Lunar Thermogravimetric Analyzer(LTGA) [JAXA] | It will observe Mineralogical and elemental measurements of the drilled samples |
| (b) Triple Reflection Reflectron (TRITON) [JAXA] | It will identify the chemical species of the volatile component in the drilled samples based on mass spectrometry. | |
| (c) Aquatic Detector using Optical [JAXA] | —— | |
| (2) Resonance ( ADORE ) | (a) ISRO Sample Analysis Package (ISAP) [ISRO] | It will observe Mineralogical and elemental measurements of the drilled samples |
| (b) Advanced Lunar Imaging [JAXA] | —– | |
| (3) Spectrometer(ALIS) | (a) Neuron Spectrometer(NS) [NASA] | Observe underground neutron (hydrogen) up to 1 meter during rover traverse |
| (b) Ground Penetrating Radar(GPR) [ISRO] | It is used to observe up to a depth of 1.5 meters during a rover traverse | |
| (c) Exospheric Mass Spectrometer for LUPEX (EMS-L) [ESA] | It will measure surface gas pressure and chemical compositions | |
| (d) Mid-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer [ISRO] | —– |
Expectation from LUPEX
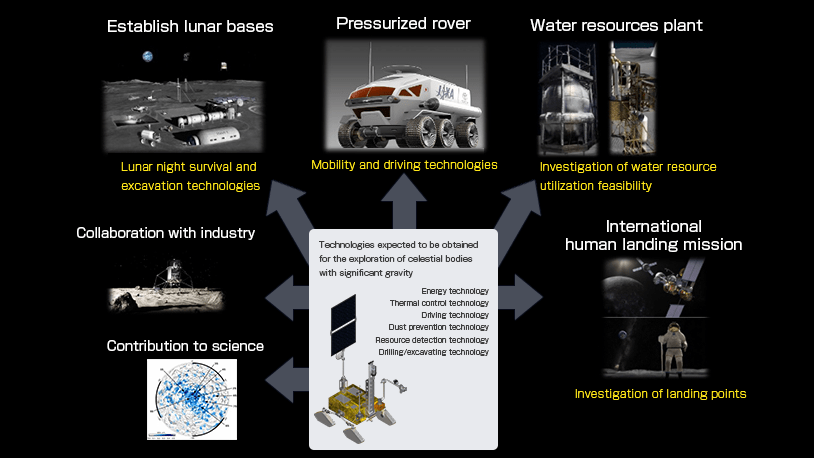
Expectations from LUPEX are very high its success paved the path to establishing a Lunar base, an International human landing mission, collaboration with industries, and the development of a pressurized rover for human transportation on the moon.
Technology will be used in LUPEX
To achieve these objectives, LUPEX will deploy a cutting-edge spacecraft equipped with thin-film solar cells and ultra-high-energy-density batteries. This spacecraft will ensure an uninterrupted power supply even in lunar regions with constant darkness or shadow. These technological innovations are crucial for the rover’s mobility and survival in the challenging lunar environment.
LUPEX aims to advance the necessary technology for exploring low-gravity celestial bodies such as the moon. This includes refining mobility solutions, optimizing the lunar night survival system, and developing excavation techniques for potential mining operations. These advancements will not only support future lunar activities but also have the potential to impact missions beyond the Moon, including Mars and beyond.
Read also NGLV: Next Generation Rocket for India’s Space Station by 2035
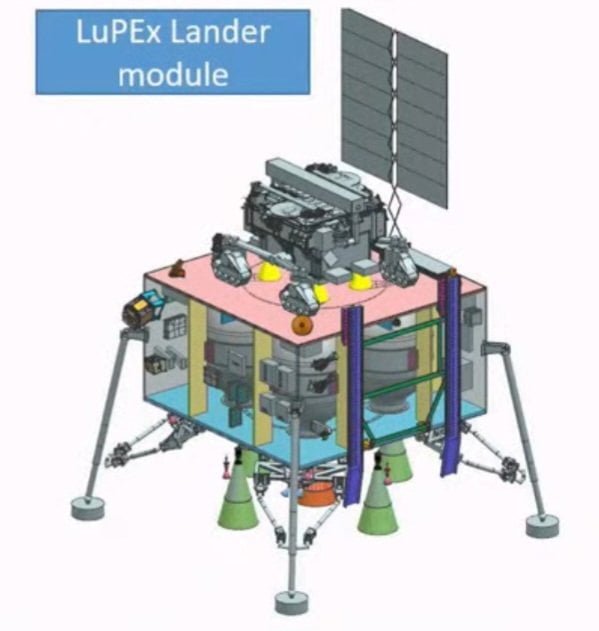
Lander of LUPEX
It is confirmed by ISRO, that ISRO will provide a Lander for this mission which will carry three science instruments including a ground penetrating radar and a 350 kg rover will be provided by JAXA.

Read also Chandrayaan 3 status: Live tracking and Location
Read also SPADEX – A step toward India’s Space Station
Who will provide the lander for the LUPEX mission?
ISRO will provide a Lander for this mission which will carry three science instruments including a ground-penetrating radar

