On January 2nd, 2024, SpaceX achieved a significant milestone by successfully launching its first batch of direct-to-mobile-phone Starlink satellites with the most reliable Falcon 9 rocket. These satellites are specifically designed to establish direct connections with unmodified smartphones, marking a leap forward in satellite internet technology.
The primary goal is to offer direct-to-cell capabilities, revolutionizing the way we access the internet on our smartphones. With this advancement, SpaceX aims to provide widespread satellite broadband coverage, promising a future where seamless connectivity is not limited by geographical constraints.
SpaceX is set to deploy a total of 840 direct-to-cell Starlink satellites, with the initial batch of six satellites already launched. These satellites were sent into space after securing a temporary experimental license to start testing their abilities in the United States.
The initial direct-to-cell service will kick off with text messaging, with plans to expand to include voice and data capabilities in the coming years. However, it’s important to note that the company still awaits regulatory approval to offer these services commercially.
In August 2022, a U.S. wireless carrier announced plans to use SpaceX’s Starlink satellites for mobile network access. This collaboration extends globally, with providers like Japan’s KDDI, Australia’s Optus, and Canada’s Rogers joining forces. SpaceX has already facilitated reciprocal access for various providers, including T-Mobile and Rogers, showcasing the increasing global adoption of direct-to-cell technology.
How does direct-to-mobile-phone satellite work?
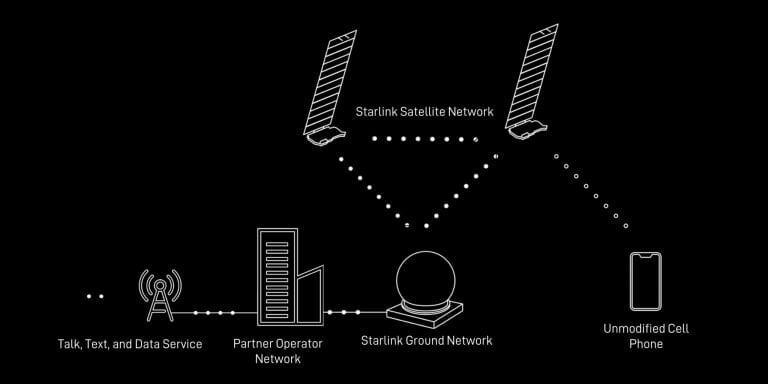
The essence of how direct-to-mobile phone satellite technology works lies in its transformative impact on internet access for smartphones. SpaceX’s primary goal is to revolutionize this access by offering direct-to-cell capabilities, breaking free from geographical constraints, and providing widespread satellite broadband coverage. This advancement promises a future where connectivity is seamless and universally accessible.
In practical terms, direct-to-cell technology operates with LTE phones, essentially acting as a space-based cell phone tower. This implies that service becomes available across all locations as long as there’s an active signal from the satellite. Remarkably, no external connections or additional hardware are necessary for users to benefit from this convenience.
The satellites equipped with Direct Cell capability feature an advanced eNodeB modem onboard, functioning akin to a cellphone tower in space. This enables network integration similar to a standard roaming partner, ensuring efficient and reliable connectivity. In summary, the direct-to-cell satellite system by SpaceX represents a cutting-edge approach that redefines how we connect, promising a future of enhanced accessibility and seamless communication.
Limitations of Direct-to-Cell
Bad weather, such as intense rain and heavy snowfall, can mess with direct-to-cell satellite services, it’s usually just a temporary glitch, and things get back to normal on their own.
How it differs from JioSpace Fiber
The major distinction lies in the fact that Direct to Cell doesn’t need any extra equipment; satellites link up directly to smartphones without any added hardware. This means smartphones can roam freely without any limitations. On the other hand, JioSpace Fiber requires some additional gear, like a dish antenna and a router, to connect to a smartphone, and it has a limited range for a better connection.
Read the full article JioSpaceFiber: India’s 1st satellite-based internet service and how it works
Read also Skyroot Aerospace: India’s SpaceX


