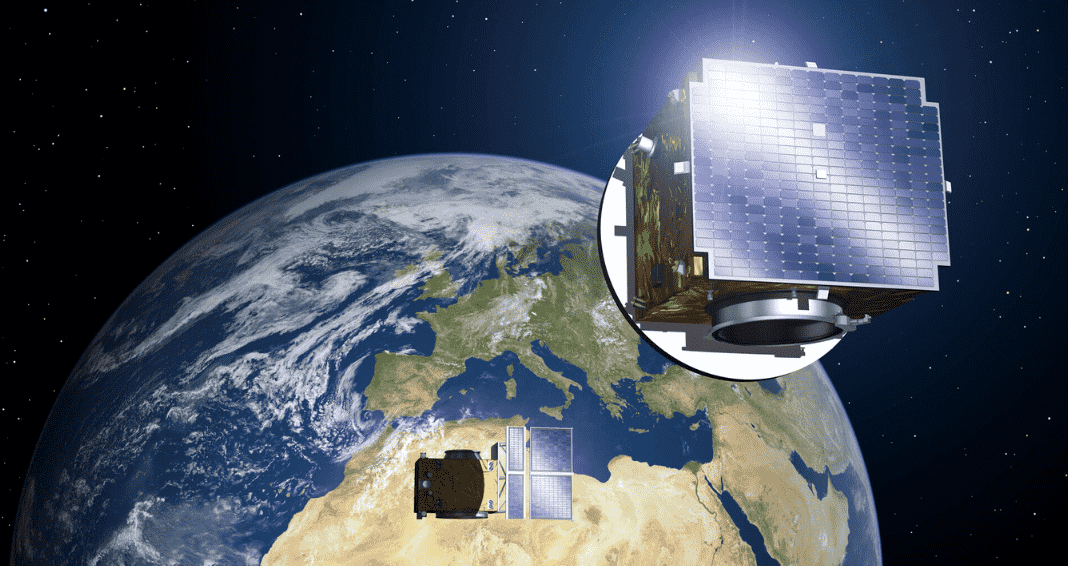
Indian Space Research Organisation set to launch the European Space Agency’s Proba-3 mission by PSLV-XL in September 2024 from Shri Harikota, Andhra Pradesh. PROBA ( Project for On-Board Autonomy ) is a minisatellite technology demonstration mission designed to tackle challenges related to the on-board operational autonomy of a generic platform.
Proba-1 was also launched by ISRO’s PSLV on 22 October 2001. PROBA is the designated name for a series of satellites, commencing with PROBA-1. The term is also utilized to denote the satellite bus within this series.
All about Proba-3 Mission
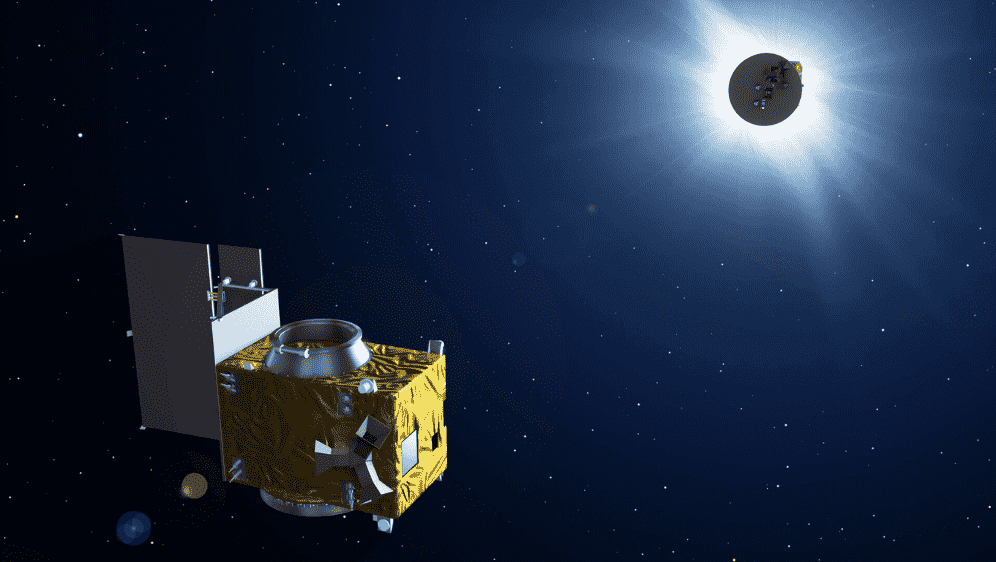
The Proba 3 mission comprises two small satellites: a coronagraph spacecraft and an occulter spacecraft shaped like a solar disc. Both satellites are flying closely together, maintaining a distance of about 150 meters. The Occulter satellite is positioned to accurately cast its shadow onto the Coronagraph’s telescope, effectively blocking the direct sunlight from the Sun. This unique setup allows the Coronagraph to capture detailed images of the faint solar corona in visible, ultraviolet, and polarized light for extended durations.
The success of the mission depends on accurately positioning and coordinating the two spacecraft. To accomplish this, ESA has pioneered a range of advanced technologies, such as precision cold gas thrusters and vision-based detection systems. These advancements will empower the satellites to uphold their relative positions with millimeter-scale accuracy.
Utilizing precise millimeter-scale formation flying, the paired satellites of Proba-3 will achieve what was once considered an impossible feat in space missions: casting a meticulously controlled shadow from one platform to the other. In doing so, they effectively block the intense rays of the Sun, enabling prolonged observation of the ethereal surroundings of its ghostly atmosphere.
Researchers anticipate that Proba-3 mission’s distinctive perspective will offer fresh perspectives on the origins of coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which are solar eruptions capable of disrupting satellites and power grids on Earth. The mission will additionally measure total solar irradiance, monitoring variations in the Sun’s energy output that could impact Earth’s climate.
Read also Shukrayaan 1: India’s next mission to Venus
| Launch Date | September, 2024 |
| Mass | coronagraph spacecraft 340 kg, occulter spacecraft 200 kg |
| Orbit | High Earth orbit, 19.7 hours orbital period, 60 530 km apogee, 600 km perigee |
| Instrument: | External coronagraph |
| Ground station | Mission antenna will be at Santa Maria des Azores, and ground station at Redu, Belgium |
The partnership between ESA and ISRO, highlighted by the collaboration on the Proba-3 mission, exemplifies the increasing trend of international cooperation in space exploration. By combining resources and expertise, these organizations, along with the utilization of the ISRO rocket PSLV-XL, are collectively pushing the boundaries of what’s achievable in the realm of space endeavors.
Read also Indian Space startup building fuel station in Space!