Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is developing a new rocket RLV (Reusable Launch Vehicle ) named as that can be used repeatedly for satellite launches and for launching humans into space. The new rocket looks like NASA’s space shuttle that used to send astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS).
It is in the developing phase as RLV-TD (Reusable Launch Vehicle – Technology Demonstrator) Once it will complete then satellite launch costs will be significantly reduced, and India join the race of space tourism with several other space companies like Blue Origin and Space-X, SSLV is also a new rocket of ISRO that will be reduced the launching cost of satellites.
What is a Reusable Launch Vehicle
A Reusable is a type of rocket that is used for launching satellites and humans into space again and again, just like an airplane puts the payloads in an RLV (Reusable launch vehicle) for the next mission after some maintenance.
The conventional rocket just like PSLV, GSLV consists of 4 and 3 stages respectively, and these stages are shed one by one after fuel is exhausted only the first stage (lowermost part) can be used again if it lands safely on Earth by using parachutes, and other separated stages will float in space as debris. These rockets are manufactured for every new mission. whereas reusable launch vehicles will once be manufactured and used again and again so RLV will reduce the launching cost and make satellite launching costs very economical and also help to reduce space debris.
Falcon-9 rocket is the world’s first operational reusable and most successful rocket, it was designed and developed by Space-x in 2010, it is a 54-meter tall two-stage rocket that is capable of transporting crew and payloads to the Internation Space Station (ISS) but practically it is not a completely reusable rocket only first stage is reusable and second stage will float in space as debris. The first stage of Falcon-9 will return after separation from the main rocket and land vertically on the landing site with the help of inbuilt engines.
What is special in ISRO’s RLV
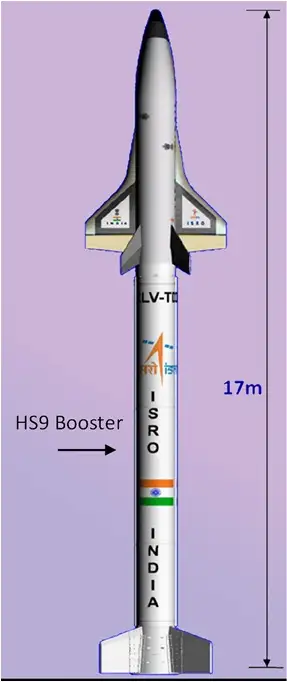
ISRO is developing a fully reusable launch vehicle RLV-TD (Reusable Launch Vehicle – Technology Demonstrator) since 2012, that is a two-stage-to-orbit (TSTO) launch vehicle, 1st stage is like a rocket and its 2nd stage is similar to an airplane, it is a combination of an airplane and a launch vehicle. 2nd stage of the Indian reusable launch vehicle uses a Scramejet (Supersonic combusting ramjet) engine that collects air for combustion from the atmosphere at supersonic speed.
After the launch of RLV, the first stage will separate after fuel is exhausted and land vertically by using parachutes or an inbuilt engine at the landing site, 2nd stage will proceed towards deploying payloads in the designated orbit and return to earth and land horizontally on a landing strip by using landing gears like an airplane. Both stages will be ready again for flying after some maintenance.
ISRO’s RLV will take off vertically like a rocket, return to Earth, and land on an airstrip as an airplane this is the unique feature of an Indian reusable launch vehicle.
Read also Chandrayaan 4: Unlocking Lunar Mysteries Beyond Soft Landing
Developments of RLV-TD
RLV-TD (Reusable Launch Vehicle – Technology Demonstrator) is a scaled-down prototype of the actual RLV that ISRO is developing. This program started in 2012 to develop a fully reusable launch rocket in four phases.
| Test | Date |
| HEX (Hypersonic Flight Experiment) | 23 May 2016 |
| LEX (Landing Experiment) | 2 April 2023 |
| REX (Return Flight Experiment) | To be Announce |
| SPEX (Scramjet Propulsion Experiment) | To be Announce |
The first atmospheric test flight of this prototype called HEX (Hypersonic Flight Experiment )was conducted by ISRO on 23 May 2016 which reached a maximum altitude of 65 kilometers and lasted for 770 seconds to evaluate various technical parameters like autonomous navigation and guidance, reusable thermal protection system, and re-entry mission management at hypersonic speed.
2nd successful test of this prototype was conducted on 2 April 2023 which was the Landing Experiment (RLV-LEX), this test prototype reached a height of 4.5 km as an underslung by an Indian Air Force Chinook helicopter and helicopter drop RLV prototype from that height to conduct an autonomous landing (unmanned precise landing ) by following return path as if vehicle return from space to evaluate technical parameters on more than 10 points like sink rate of landing gears, ground relative velocity, and precise body rates.
This project is developing under the collaboration of ISRO, DRDO, HAL, and IAF. Most important DRDO will be able to develop a hypersonic missile after some modifications to this RLV design.
Why does India need RLV?
Globally Falcon-9 of Space-x is the only operational reusable rocket, so launching satellites by reusable rocket is very economical, NASA is also using Falcon-9 rockets for cost-cutting in satellite launching. The satellite launching market is a multimillion-dollar market and growing at a pace, this market will be captured by those who launch satellites at a very low price and this competition will grow in the future. At present this market is captured by Elon Musk’s Space-x.
Japan’s JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), China’s CNSA (China National Space Administration), and Russian ROSCOSMOS are developing their reusable launch vehicle so India is also required to develop their reusable launch rocket and capture the market & stay ahead of the competition. by this rocket India will join the race of Space tourism, It is expected that India will develop its Space shuttle, or RLV by 2026.
RLV vs Falcon-9
Indian RLV is a two-stage-to-orbit (TSTO) and fully reusable rocket whereas Falcon-9 is also a two-stage-to-orbit rocket but not fully reusable only the first stage of this rocket is reusable.
Indian RLV is designed for small and medium satellites whereas Falcon-9 is a heavy-duty rocket that can transport cargo to the International Space Station(ISS).
Indian RLV is designed to launch satellites in LEO (Lower Earth Orbit ) about 400 km orbit whereas Falcon-9 can transport payloads to LEO (Lower Earth Orbit) and to GTO (Geostationary transfer orbit).
SSlV vs RLV
SSLV (small satellite launch vehicle) and RLV (reusable launch vehicle ) both are designed to launch small and medium satellites and reduce the launching cost. RLV will be more economical if used with full potential as compared with SSLV because relaunching RLV required only fuel cost and some maintenance cost whereas SSLV required remanufacturing of the whole rocket for relaunch.
Budget of RLV-TD or Indian Space Shuttle
An initial budget of RLV-TD was 95 crore for 5 years.
How much does ISRO charge for space tourism?
Once ISRO’s RLV will developed Space tourism will be possible and it is expected 6 crore rupees in ticket costs per person.
Read Also

