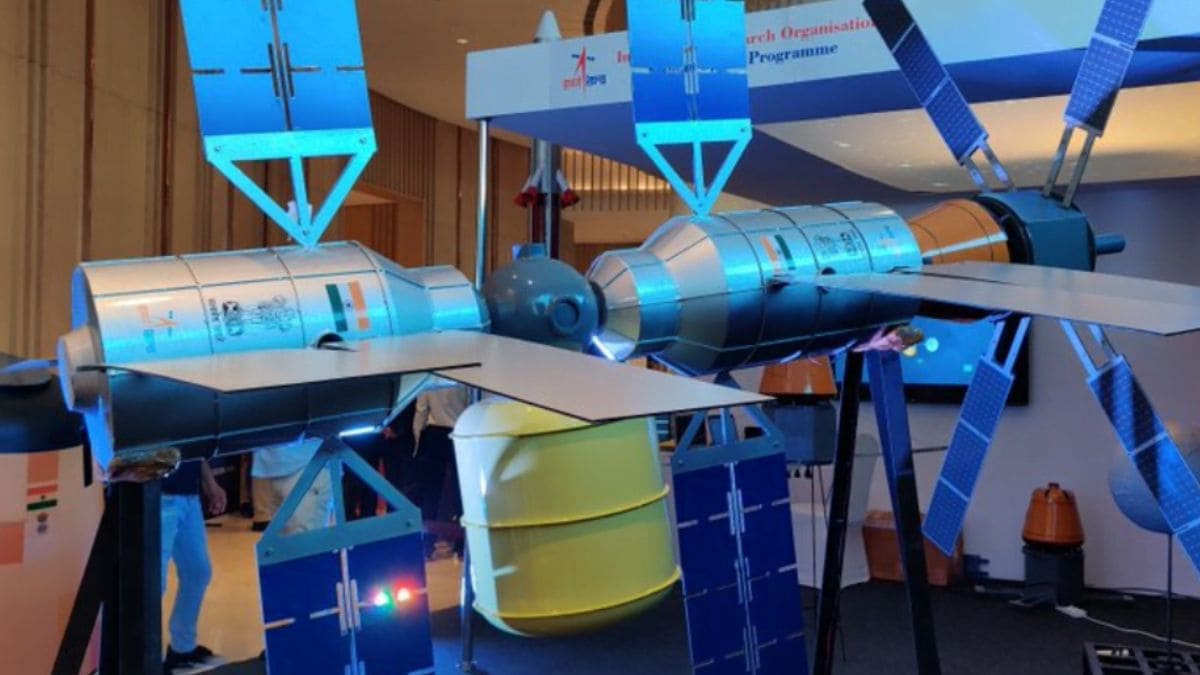
ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) is working on the SPADEX technology means Space Docking Experiment, docking is the process of connecting two free-flying spacecraft in space, either to transfer people or cargo from one to another or two free-flying spacecraft join each other to make a single bigger object best example of docking is the cargo spaceship connecting to ISS (International Space Station) for material transfer.
ISRO had launched the Spadex mission on 30th December 2024, from Satish Dhawan Space Centre By PLSV rocket. Two satellites SDX01(SpaDex -A) and SDX02(SpaDex-02) each weight around 220kg injected into two different orbit.
These satellites posses unique capability to unite or separate into two distinct pieces in space. These two components, referred to as the chaser and the target, will subsequently rendezvous and dock together, effectively combining to create a unified satellite. This pioneering technology, involving the separation and reunification of satellite components, marks a novel advancement in India’s space exploration endeavors.
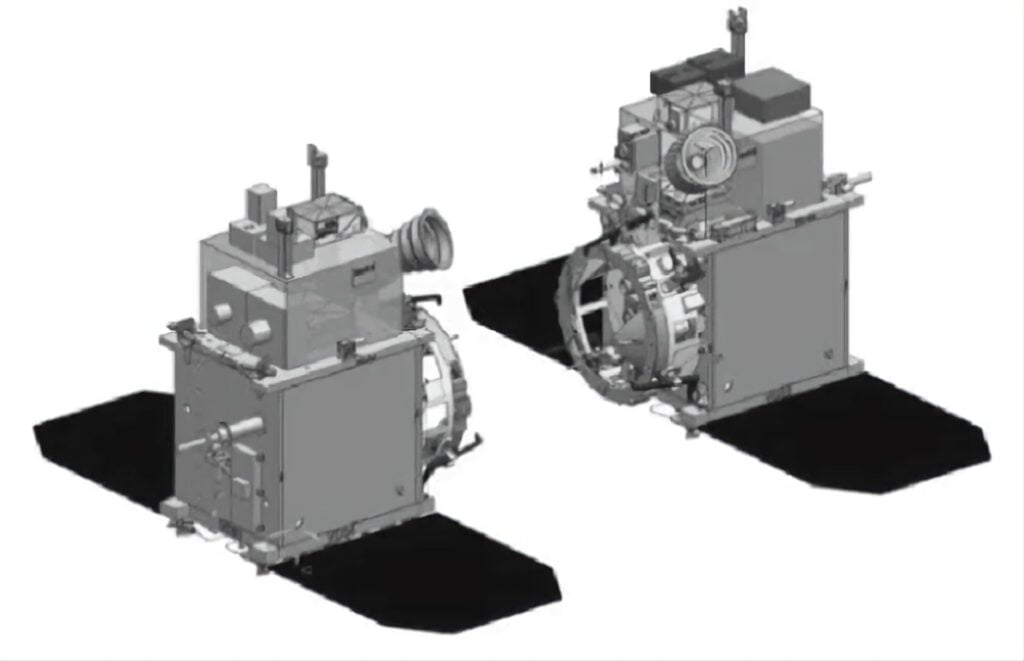
The chaser satellite will be equipped with cameras and sensors that will allow it to track the target satellite. Once the target satellite is in range, the chaser will dock with it using a robotic arm. The two satellites will then be joined together by a docking mechanism. Once the two satellites are docked, they will become a single, fully functioning satellite.
This split-up and united technology has the potential to revolutionize the way satellites are launched and operated. In the past, satellites have been launched as single, monolithic units. This has made them difficult and expensive to repair or upgrade. With the split-up and united technology, satellites can be launched in smaller pieces, which are easier and cheaper to transport. If a satellite needs to be repaired or upgraded, only the affected piece needs to be replaced. This can save a significant amount of time and money.
ISRO is hoping that the split-up and united technology will pave the way for new and innovative satellite applications. For example, the technology could be used to create constellations of satellites that can work together to provide better coverage and performance. It could also be used to create satellites that can be customized for specific missions.
The launch of the split-up and unite satellite is a major milestone for ISRO. It is a sign that the organization is at the forefront of space technology. The success of this mission could have a significant impact on the future of satellite development.
Post Mission
After docking and undocking both satellites SDX01(SpaDex -A) and SDX02(SpaDex-02) will separate and work independently with different objective. SDX01 has a high Resolution Camera (HRC) with a 4.5 meter Instantaneous Geometric Field of View from a 450 km altitude. This will act as surveillance camera from Space. Where as SDX02 has miniature multi -Spectral Payload (MMX) and Radiation Monitor (RadMon) payload.
Read Also NGLV: Next Generation Rocket for India’s Space Station by 2035
Objective of SPADEX
(1) To demonstrate autonomous rendezvous and docking of two spacecraft in low Earth orbit.
(2) To develop and validate technologies for the formation of flying two spacecraft.
(3) To demonstrate remote robotic arm operations.
(4) To develop and validate technologies for controlling one spacecraft with the attitude control system of another spacecraft.
SPADEX will be a milestone in the creation of India’s Space Station. China already created its own Space Station Tiangong.
SPADEX For Bhartiya Antariksha Station

ISRO intends to conduct a space test of the technology during the Spadex mission scheduled for 2024. This technology serves as the initial building block for the Indian Space Station, also referred to as the ‘Bhartiya Antariksha Station.’ The first module of the station is planned for launch in 2028, utilizing the LVM3 rocket.
Every space station is constructed through the assembly of smaller units that are docked together to form a larger structure, a process observed in the construction of the International Space Station (ISS). With the application of this technology, ISRO aims to finalize the construction of the ‘Bhartiya Antariksha Station’ by the year 2035. This involves integrating all modules dispatched by ISRO from Earth between 2028 and 2035. Additionally, the utilization of this technology enables the potential for further extensions to the station in the future.
Read also Indian Space Station: ISRO to launch Bhartiya Antariksha station by 2028
SPADEX For Chandrayaan-4

Chandrayaan-4 emerges as ISRO’s subsequent mission following the achievements of Chandrayaan-3. The mission is designed to execute a gentle touchdown on the lunar surface, gather lunar samples, and subsequently make a return journey to Earth, bringing back the collected lunar samples. A crucial component of this mission involves the application of SPADEX technology, which facilitates the docking process. This technology is instrumental in coordinating the rendezvous between a spacecraft, launched from the lunar surface post-sample collection, and the sample return module orbiting in space, ensuring the successful transfer of lunar samples.
Read also Chandrayaan 4: Unlocking Lunar Mysteries Beyond Soft Landing
SPADEX For Ganganyaan 2 and NASA’s Artemis mission

Gaganyaan 1 is an ISRO mission aimed at sending three Indian astronauts into space, placing them in an orbit 400 km above Earth for a duration of 3 to 7 days. Gaganyaan 2 is planned to send Indian astronauts to the Bhartiya Antariksha Station after its expected completion in 2035. The mission also includes the ambitious goal of landing humans on the moon in collaboration with NASA’s Artemis moon base, with a targeted timeline set for the year 2040. Here, SPADEX technology will be utilized for docking spacecraft with both the Indian space station and the Artemis moon base.
Application of SPADEX
Through these experiments, ISRO will be able to do many kinds of tasks.
(1) ISRO will be able to transfer humans from one spaceship to another ship in space
(2) Refueling of a spaceship in space just like air-to-air refueling of a jet
(3) Crucial cargo can be shifted from one spaceship to another spaceship
(4) ISRO will be able to replace a part of an existing satellite in orbit
Read also Indian Space startup building fuel station in Space!
Budget of SPADEX
The budget for the SPADEX mission is 124.47 crore (US$16 million). This budget covers the cost of developing and launching the two spacecraft, as well as the cost of ground support and operations.
The budget for the SPADEX mission was approved by the Government of India in July 2022. The mission is scheduled to launch in the third quarter of 2024.
Here is a breakdown of the SPADEX mission budget:
- Spacecraft development: 68.47 crores (US$9 million)
- Launch vehicle: 30.00 crore (US$4 million)
- Ground support and operations: 26.00 crores (US$3 million)
Read also India’s 1st Private Satellite Launch Station
Read also RLV: ISRO’s new rocket for space tourism
Read also NavIC: India’s powerful GPS-like system
When will India have its own Space Station?
It is expected that India will have its own Space Station by 2035. ISRO is working on this by doing experiments like SPADEX and developing an NGLV rocket.
When will ISRO launch the SPADEX Mission?
ISRO is planning to launch the SPADEX Mission in 2024.